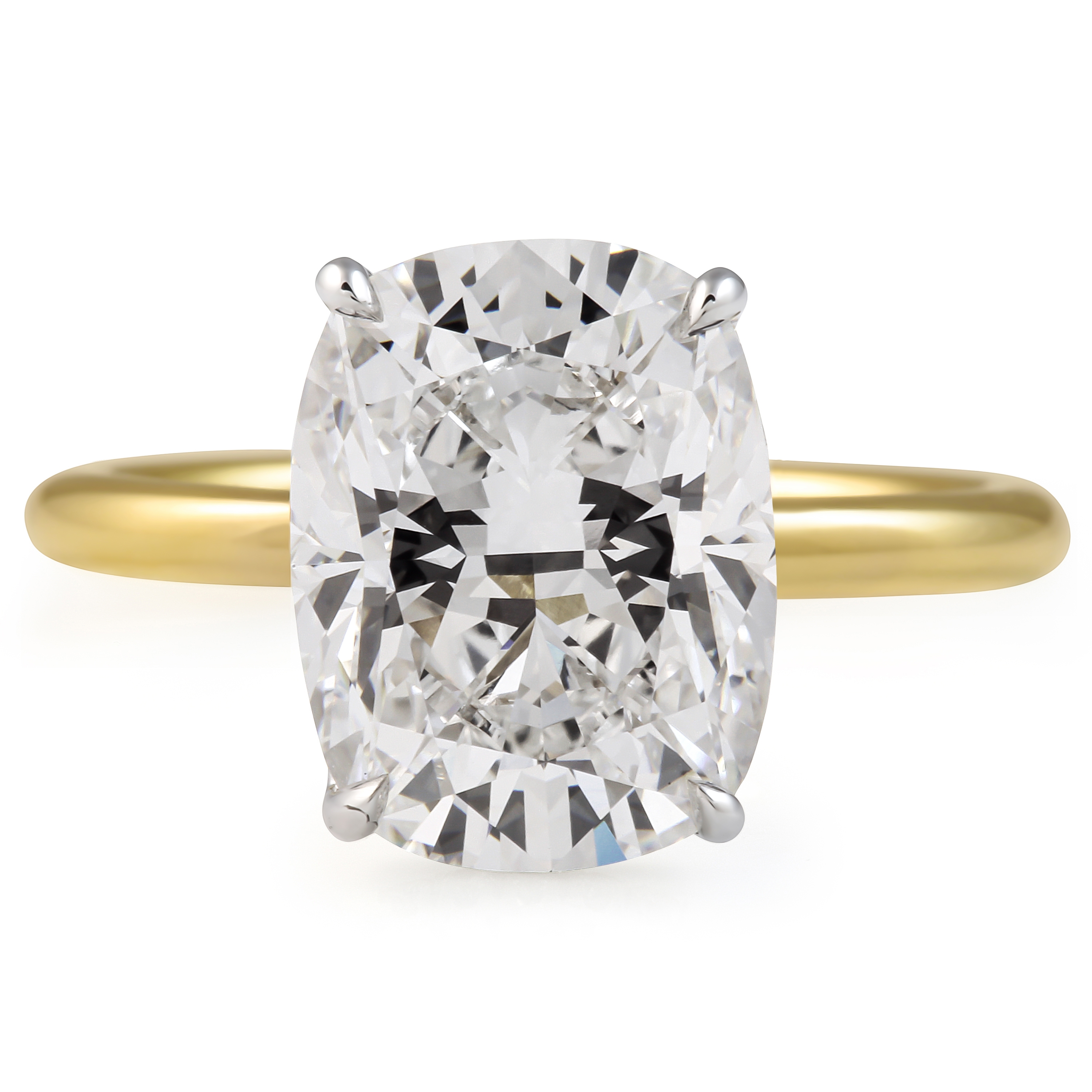
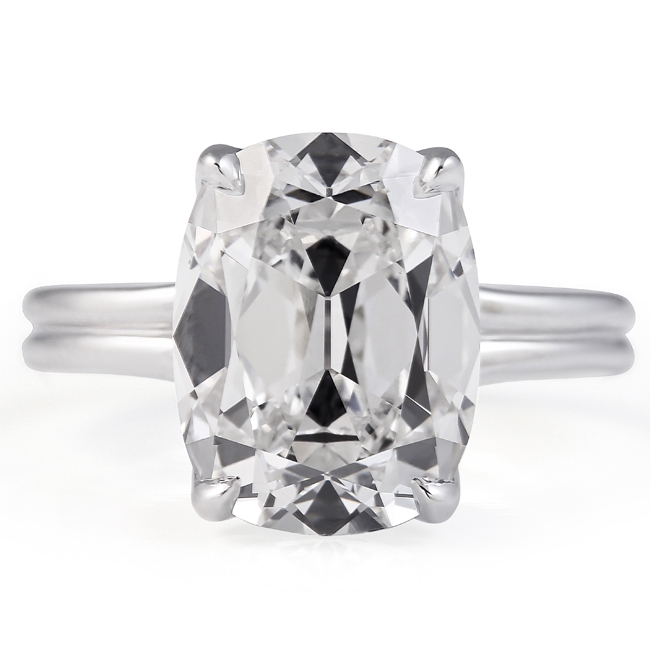
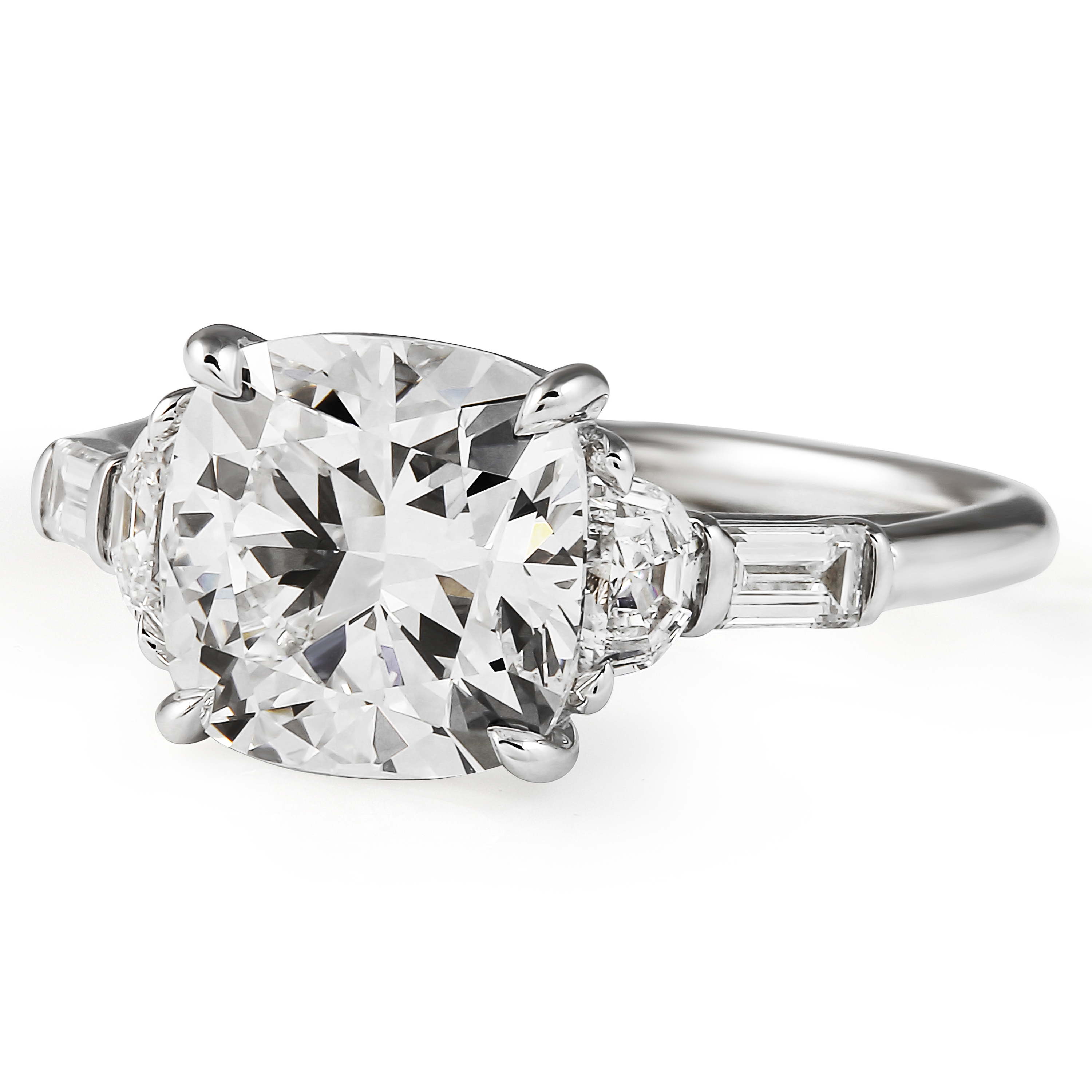
Cushion Cut Lab Diamond Engagement Rings
Cushion cut diamonds are ultra-feminine, soft, and delicate with a pillow-like shape and a dazzling sparkle. The soft shape of this cut and its substantial surface area on the finger has made lasting impressions.


View Some our Favorite Cushion Cut Lab Diamond Engagement Rings
Meet with us in-store at our New York City showroom or shop with us remotely to see more Cushion Cut Lab Diamond Engagement Rings.
- In-Store
- Virtual
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a cushion cut diamond?
The cushion cut diamond is classified by its square or rectangular shape with soft, rounded edges, which takes on a pillow-like appearance. The faceting of a modified brilliant cushion cut diamond places emphasis on brilliance and sparkle, while effectively hiding diamond imperfections and diamond color.
How is a lab-grown cushion-cut diamond created?
There are two methods to create lab diamonds: High Pressure High Temperature (HPHT) and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). Once the rough lab diamond has been created, depending on the size, the lab plans out which cut(s) and sizes can be cut from the rough diamond.
What is the best clarity for a lab-grown cushion-cut diamond engagement ring?
Depending on the types of inclusions, SI2 and above can be acceptable for cushions.
Does a lab-grown cushion-cut diamond possess the same optical properties as a natural diamond?
All lab grown diamonds possess the same optical and chemical properties as their natural counterparts. The only difference between natural and lab diamonds is where they were physically formed and how long it took for them to form.
Are there different types of cushion cuts?
Cushion cut diamonds have several cut styles that reveal a slightly different overall appearance from style to style: Cushion Brilliant, Cushion Modified, and Antique Cushion (Old Mine Cut).
What’s the difference between a modified cushion cut and an antique cushion cut?
Cushion cuts offer a soft, feminine experience due to the rounded edges, but they deliver plenty of fire thanks to the defined facets. However, if you want larger facets and the maximum amount of sparkle, the modified brilliant cushion cut is the option; these diamonds are cut to maximize refraction and shine whereas antique cushion cuts are not.The primary difference between modified brilliant and antique cushion cuts is the faceting: while they both have “larger” faceting, antique cushion facets are the only cut with “chunky” facets. Additionally, antique cushions feature an open, visible culet at the bottom and a steeper crown where modern brilliant cushion cuts do not.
How is a lab-grown diamond created?
There are two methods to create lab diamonds: High Pressure High Temperature (HPHT) and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).HPHT was the first major method for creating lab-grown diamonds. It mimics the natural process of diamond formation in the span of a several weeks as opposed to several billion years. A diamond seed is placed into a special press with carbon. The area is until it reaches a temperature of around 1600 degrees Celsius, or about 2900 Fahrenheit. The chamber exerts pressure up to and over 870,000 pounds per square inch. Molten metal (typically from a source like graphite) in the chamber then dissolves the carbon source, and a diamond begins to form and build around the diamond seed.In CVD, a diamond seed is placed into a sealed vacuum chamber. After the chamber fills with carbon-heavy gas, like methane, it’s heated to a high temperature of around 1500 degrees Fahrenheit. The high temperatures convert the gas into plasma, which releases pieces of carbon. Those carbon pieces build upon the diamond seed originally placed in the chamber. Eventually, a full diamond forms after layer and layer of carbon pieces attach to the seed. The whole process produces incredible, chemically-pure diamonds free of most impurities. They don’t contain metal inclusions, either.You can read more about HPHT and CVD in our blog, An In-Depth Look at CVD vs. HPHT.
What’s the difference between lab-grown diamond engagement rings vs natural diamonds?
Natural diamonds form over millions of years under pressure from the Earth’s crust, and are mined, cut, and polished to produce the brilliant stones you find in jewelry. Lab-grown diamonds undergo the same process, only instead of millions of years, they form in a few weeks via a high temperature or a chemical vapor process. The difference between a natural and lab-grown diamond is indistinguishable to the naked eye. They have the same chemical and physical attributes, but specially trained gemologists may be able to use a magnifying tool to indicate growth patterns or the presence of elements that would help distinguish one from the other. However, the most trusted method is to use a testing machine. Both types can have inclusions, or tiny flaws, but have identical hardness.
Are lab-grown diamonds GIA-certified?
Not all lab-grown diamonds are GIA certified. However, all lab-grown diamonds at Lauren B are GIA certified! Browse our inventory of GIA Graded lab diamonds.
Are lab-grown diamonds as durable as natural ones?
Natural and lab created diamonds have the exact same chemical composition. Because of this, lab diamonds are also just as durable as natural diamonds meaning they are the hardest, most durable gemstone on the Mohs scale.
Learn More Here: